Automotive Resistors And Power Resistors In Modern Vehicles
Automotive resistors are essential components used to control current, regulate voltage, and protect electronic systems in modern vehicles. As vehicles become more electrified and intelligent, power resistors and other automotive-grade resistors play an increasingly important role in ensuring system reliability and safety.
Designed for harsh environments, automotive resistors must operate reliably under high temperature, vibration, and electrical stress, making them very different from standard commercial resistors.
1.What Are Automotive Power Resistors?
Automotive power resistors are designed to handle higher power dissipation while maintaining stable electrical performance. They are commonly used in applications where energy control, heat management, and current regulation are critical.
Typical applications include:
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid systems
- DC-DC converters and inverters
- Motor control and braking systems
- Battery management systems (BMS)
These resistors are often engineered with low TCR, high thermal stability, and robust mechanical structures to meet automotive reliability requirements.
2. Main Types of Automotive Resistors
(1) Shunt Resistors (Current Sense Resistors)
Shunt resistors measure current by detecting the voltage drop across a low resistance value.
They’re crucial in battery management systems (BMS), EV powertrains, alternators, and DC/DC converters.
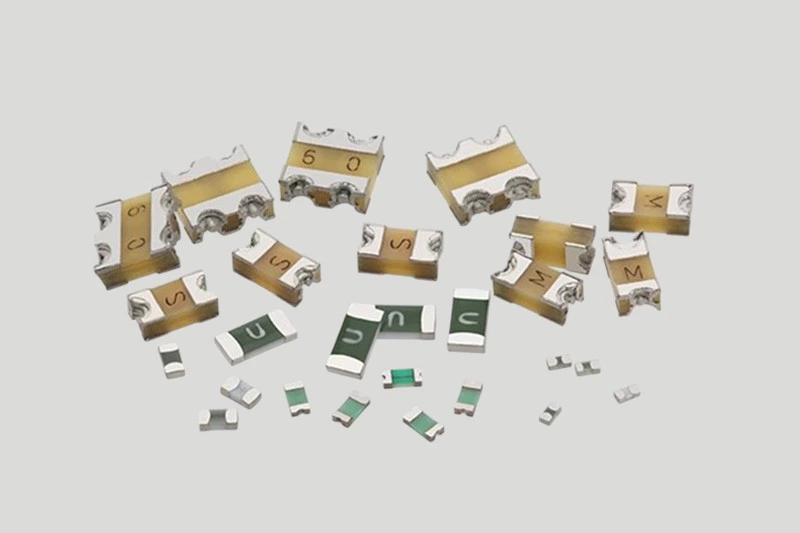

(2) Chip Resistors (SMD Type)
Surface-Mount (SMD) resistors are widely used in compact automotive circuits for ECUs, sensors, and communication modules, offering miniaturization and automation-friendly assembly.
(3) Thick Film Resistors
Used for general signal and control circuits, thick film resistors offer high stability, compact size, and cost efficiency. Applications include ECUs, lighting systems, and infotainment devices.
(4) Thin Film Resistors
Known for precision and low temperature coefficient, thin film resistors are suitable for measurement, sensor, and communication modules where accuracy is critical. Common in ADAS sensors, communication modules, and audio circuits.
(5) Metal Film Resistors
These resistors feature excellent accuracy and low noise, ideal for analog and precision control circuits, such as engine management systems.
(6) Wirewound Resistors
Built from coiled resistance wire, wirewound resistors handle high current and power dissipation.
Used in power steering units, braking systems, and heater controls.
3. Functions of Resistors in Automotive Circuits
- Current Limiting: Protects devices like LEDs and ICs from excessive current.
- Voltage Division: Provides reference voltage for signal conditioning and sensing.
- Current Sensing: Measures current flow for system monitoring and control.
- Load Balancing: Distributes power evenly across parallel circuits.
- Heat Dissipation: Converts surplus electrical energy into heat for stability.
- Signal Conditioning: Filters noise and stabilizes signals in communication circuits.
4. Applications in Vehicle Electronics
Automotive and power resistors are used across a wide range of vehicle systems, including:
- Electric and hybrid powertrains
- ADAS and safety systems
- Body control modules
- Infotainment and comfort electronics
They help ensure stable operation, accurate sensing, and effective power management throughout the vehicle.
5.Why Automotive-Grade Resistors Matter
Automotive environments expose components to extreme temperature changes, vibration, and electrical stress. Using qualified automotive-grade resistors improves system durability, safety, and overall performance.
As vehicles continue to evolve toward electrification and intelligent control, reliable automotive and power resistors remain a fundamental part of modern vehicle design.
Conclusion
From simple voltage division to complex current sensing in electric vehicles, automotive resistors are the backbone of reliable and efficient automotive electronics. Selecting the right resistor type—based on precision, power, and temperature performance—is essential to achieving long-term stability and safety in modern vehicles.
