Differences between Polymer ESD devices and conventional ESD protectors
Introduction to ESD

1.Definition
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) protection devices are mainly composed of arrays of TVS (Transient Voltage Suppression) diodes and are packaged in various forms. They belong to the category of overvoltage clamping protection devices.
2.Materials
These devices are formed using semiconductor materials, dies, metals, and resin encapsulation.
3.Working Principle
The device is connected in parallel to the circuit. During normal operation, it remains in an off state (high impedance) and does not affect the circuit’s performance. When an abnormal overvoltage occurs and reaches the device's breakdown voltage, it quickly switches from a high-impedance state to a low-impedance state, providing a low-resistance path for the transient current. At the same time, it clamps the abnormal high voltage to a safe level, thereby protecting the IC or circuit. Once the overvoltage event is over, the device returns to a high-impedance state and the circuit resumes normal operation.
Introduction to Polymer ESD
1.Definition
A type of polymer ESD suppressor that possesses the advantages of typical ESD protection devices.
2.Materials
Made from polymer voltage-variable materials and high molecular compounds at its core.
3.Working Principle
The device is connected in parallel to the circuit. During normal operation, it remains in an off state and does not interfere with the circuit's function. When an abnormal overvoltage occurs and reaches the device's breakdown voltage, it quickly switches from a high-impedance state to a low-impedance state, providing a low-resistance path for the transient current. At the same time, it clamps the abnormal high voltage to a safe level. Once the overvoltage disappears, the device returns to a high-impedance state, and the circuit resumes normal operation.
PROSEMI Composition of ESD Products
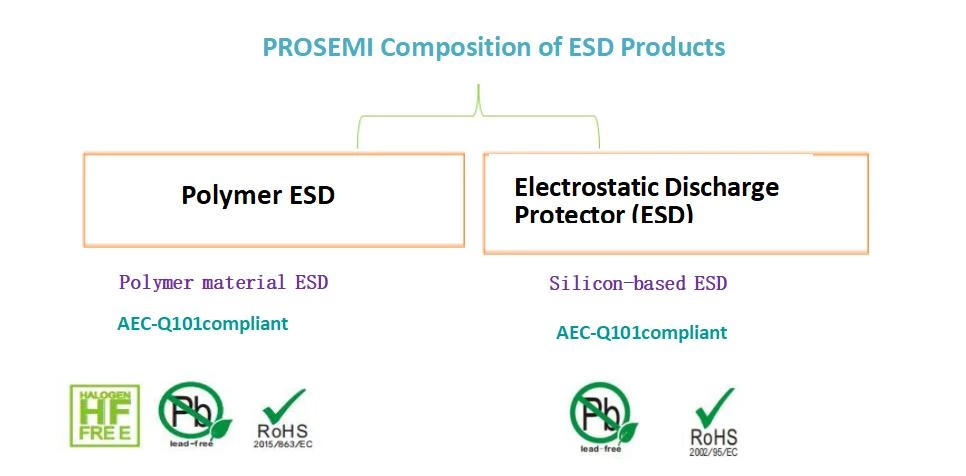
Electrostatic Protector (ESD) and Polymer ESD Selection Criteria
1.Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) protection device selection criteria
(1)Reverse Stand-off Voltage
The device’s reverse stand-off voltage should be greater than 1.2 times the circuit's normal operating voltage, with an appropriate safety margin.
(2)Capacitance
Choose the device’s capacitance based on the transmission rate of different interfaces. The higher the signal frequency, the lower the required capacitance. High capacitance can cause signal loss or packet drops.
(3)Clamping Voltage
The clamping voltage should be lower than the maximum voltage the downstream IC can tolerate.
(4)Package Type
Should be selected according to the actual requirements of the customer.
(5)ESD Protection Level
Should meet or exceed the protection level required by the application.
3.Selection Factors for Polymer ESD Protection
(1)Rated Voltage
The device's rated voltage should be greater than or equal to the circuit’s normal operating voltage.
(2)Capacitance
Select the device’s capacitance based on the transmission rate of the interface. The higher the signal frequency, the lower the required capacitance. Higher capacitance can lead to signal loss or packet drop.
(3)Claming Voltage
The clamping voltage should be lower than the maximum voltage tolerance of the downstream IC.
(4)Package Type
Should be chosen based on the customer’s actual application needs.
(5)ESD Protection Level
Should meet the required ESD protection standards for the application.
Differences Between PROSEMI Automotive-Grade ESD Protectors and Polymer ESD Devices
| Item | Prosemi Silicon-based ESD (AEC-Q101) | Prosemi Polymer ESD (UPEP2DxxTxxxx-T, AEC-Q101) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Silicon-based semiconductor materials (semiconductor die, metal, resin encapsulation) | Polymer materials (polymer voltage-induced materials and high molecular compounds) |
| Package / Automotive Grade | DFN0603, DFN1006, DFN1610, DFN2020, DFN2510, SOD-323, SOD-523, SOT-23, SOT-143 | DFN0402 and DFN0603 / Automotive grade available |
| Leakage Current | ≤1μA (lower capacitance means lower leakage; higher capacitance increases leakage) | ≤0.1μA (typical 0.01μA) |
| Response Time | <1ns | <1ns |
| ESD Protection Level | Up to 30kV contact discharge, 30kV air discharge | Up to 15kV contact discharge, 25kV air discharge |
| Capacitance | 0.15pF to several hundred pF | Typ. 0.05pF |
| Lifetime | ≥100,000 cycles | ≥100,000 cycles |
| Operating Temperature | -40℃ to 125℃ | -40℃ to 125℃ |