Application And Selection Guide Of Low-ohm Resistors In Current Detection
Low-ohm resistors are crucial for precise current detection in various applications. Selecting the appropriate resistor involves understanding the requirements of the circuit, including the maximum current, voltage, and required accuracy. Key considerations include resistor type, rated power, tolerance, and temperature coefficient. Understanding these factors can ensure reliable and accurate current measurement.
1.The working principle of resistance
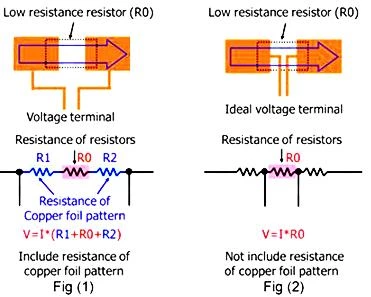
(1)The basis of Ohm's Law
- Voltage drop V = I × R.
- When current I flows through a low-ohm resistor R, the voltage drop V generated across its terminals can be sampled by an ADC, operational amplifier or a dedicated detection chip and converted into a current value.
(2)Signal amplification and processing
Due to the small size of V (usually within tens of millivolts), the downstream circuit needs to be combined with a high common-mode rejection operational amplifier or a high-resolution ADC for amplification and filtering to ensure measurement accuracy.
2.Key selection parameters
(1)Resistance value design
- The small voltage drop is balanced with the signal strength:The smaller the resistance value is, the lower the energy loss and system voltage drop will be, but the signal amplitude will also decrease accordingly.
- Typical goal:The voltage drop under the maximum current is controlled within 20 mV to 100 mV.
- Calculation method:R = V_target/I_max.
(2) Power and Thermal Management
- Power consumption calculation:P = I_max² × R.
- Safety margin:When selecting the model, leave a margin of 2 to 3 times to prevent sudden overcurrent.
- Heat dissipation strategy:Select large packages (such as 2512, 3920) or metal case resistors;Copper sheets and vias are configured on the PCB to increase the heat dissipation area.
(3)Accuracy and temperature drift
- Tolerance:±1%, ±0.5% or higher accuracy grades are recommended.
- Temperature coefficient (TCR):TCR ≤ 50 ppm/℃ can ensure stable measurement over a wide temperature range. High-precision optional ≤ 25 ppm/℃.
(4) Packaging and Layout
- SMD vs Through hole:SMD (1206, 2512) is convenient for automated production;Through-holes/studs are suitable for ultra-high current and high-power applications.
- Four-terminal Kelvin structure:Separate the current terminal from the measurement terminal to eliminate the resistance errors of the leads and pads.
- PCB Routing Principles:The wiring of the current loop should be wide and short;The measurement signal routing should avoid high-speed or high-current circuits;Place the detection amplifier or ADC near the shunt resistor to reduce noise interference.
3.Typical application scenarios
Power Supplies:
- Low-ohm resistors are essential in power supplies for monitoring current, ensuring stable operation, and protecting against overcurrents.
Battery Management Systems:
- In electric vehicles and other battery-powered systems, low-ohm resistors are used to monitor battery charging and discharging currents, optimizing performance and safety.
Motor Control Systems:
- These resistors are vital for current sensing in motor control circuits, enabling precise control of motor speed and torque.
High-Current Applications:
- In applications involving high currents, such as welding equipment or power distribution systems, low-ohm resistors are used to accurately measure and control current flow.
Precision Measurement Equipment:
- For applications requiring highly accurate current measurements, low-ohm resistors with low temperature coefficients and tight tolerances are preferred.
Smart Meters:
- Current sense resistors are used in smart meters to accurately measure the power consumption of individual appliances or the total consumption of a household.
Overcurrent Protection Circuits:
- In various electronic devices, low-ohm resistors are used to trigger overcurrent protection mechanisms, preventing damage to components and ensuring system safety.
4.Selection Example
| Application | Max Current | Target Voltage Drop | Resistance | Power Rating | Accuracy | Package Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV Battery BMS | 200 A | 50 mV | 0.25 mΩ | ≥ 20 W | ±0.5% | 4-terminal stud |
| Energy Storage System Monitoring | 100 A | 100 mV | 1.0 mΩ | ≥ 10 W | ±1% | 2512 SMD |
| Motor Drive | 50 A | 50 mV | 1.0 mΩ | 3 W | ±1% | 1206 SMD |
5.conclusion
Low-ohm resistors are indispensable core components for current detection. By rationally selecting resistance values, power, accuracy, as well as appropriate packaging and PCB layout, high-precision and low-loss real-time current monitoring can be achieved in various power electronics scenarios. Mastering the above key points will help you quickly implement a reliable current detection solution.