Prosemi Introduction To New Shallow Snapback Tvs Devices And Their Applications
PROSEMI Characteristics of Shallow Snapback TVS
Advanced Technology:PROSEMI Clamping voltage is 20% lower than the industry average.

Industry Leading:Supports both unidirectional and shallow snapback functions, while most competitors can only offer bidirectional shallow snapback.

Automotive-Grade Compliance:Designed with automotive-grade chips and certified to AEC-Q101.

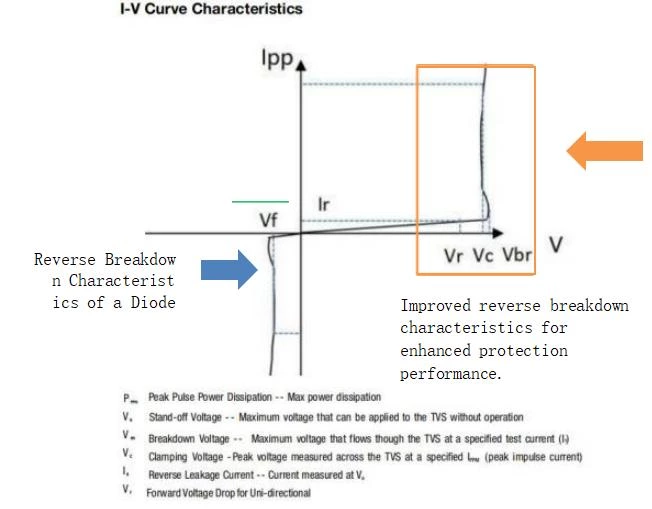
I-V Characteristic Curve of Shallow Snapback TVS
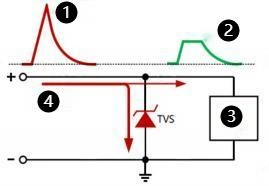
-
Transient Voltage
-
Clamping Voltage
-
Protected Circuit
-
Transient Current
Process Differences Between Bidirectional and Unidirectional Shallow Snapback
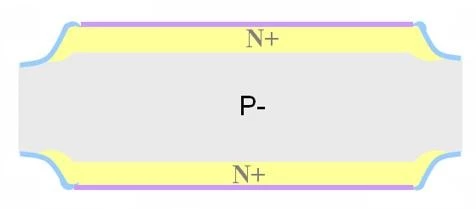
Bidirectional Shallow Snapback:
- Bidirectional low clamping voltage devices are made using P-type substrates to create bidirectional components.
- They utilize the negative resistance characteristic of silicon. The manufacturing process is the same as that of conventional bidirectional devices with N-type substrates.
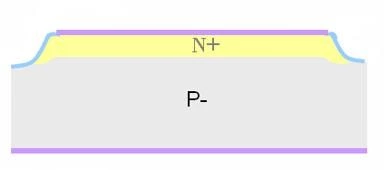
Unidirectional Shallow Snapback:
- It uses the thyristor principle, with internal junction structures fabricated on the backside. The process is longer and involves more photolithography steps.
- Through structural design, it achieves shallow snapback and high power capability. Bidirectional devices do not use this structure, mainly due to differences in the substrate.
PROSEMI Automotive BMS Lithium Battery Series Protection Solution
Typically, LiFePO4 BMS management ICs have a nominal voltage withstand of around 80V, with transient voltage withstand approximately 90V.
For ternary lithium batteries with 16-series cells, BMS management ICs usually have a nominal voltage withstand of about 100V and transient withstand around 110V.
Automotive customers require testing at 400V to 500V with a 1.2/50μs waveform. Low clamping voltage TVS devices can provide superior clamping performance under these conditions.
- Low Clamping Voltage
- Battery Pack
- Voltage Measurement and Charge Balancing IC
- Overcurrent Detection
- Overtemperature Detection
- BMS MCU
- Battery Pack+
- 12V
- CAN Communication
- Battery Pack-
| battery | 14 strings | 16 strings | Protect | Low-clamping technology | VBR center value | 10/1000μs Vc | 8/20μs@400V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lithium iron phosphate battery | Single cell 3.7V | Single section 3.2V | 3.0SMDJ75A-LC | U-nCLAMPTM | 75V | ≤85V | ≤90V |
| TPSMD64A | Traditional clamping | <103V | <133V | ||||
| Ternary lithium battery | / | Single cell 4.3V | 3.0SMDJ91A-LC | U-nCLAMPTM | 91V | ≤105V | ≤110V |
| TPSMD78A | Traditional clamping | <125V | <162V |
Electrical Parameters of Shallow Snapback TVS
| Part Number | Marking | Reverse Stand-off Voltage VR (V) | Breakdown Voltage VBR@IT (V) | Test Current IT (mA) | Max Clamping Voltage VC @10/1000µs (V/IPP) | Max Clamping Voltage VC @8/20µs (V/IPP) | Max Reverse Leakage IR @VR (μA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0SMDJ68A-LC | 3D068n | 58.1 | 64.6 – 71.4 | 1 | 72V / 41.6A | 82V / 384A | 1 |
| 3.0SMDJ75A-LC | 3D075n | 64.1 | 71.3 – 78.8 | 1 | 85V / 35.2A | 90V / 350A | 1 |
| 3.0SMDJ82A-LC | 3D082n | 70.1 | 77.9 – 86.1 | 1 | 95V / 31.6A | 100V / 314A | 1 |
| 3.0SMDJ91A-LC | 3D091n | 77.8 | 86.5 – 95.5 | 1 | 105V / 28.6A | 110V / 286A | 1 |
| 3.0SMDJ93A-LC | 3D093n | 79.5 | 89.3 – 96.7 | 1 | 107V / 28.0A | 112V / 281A | 1 |